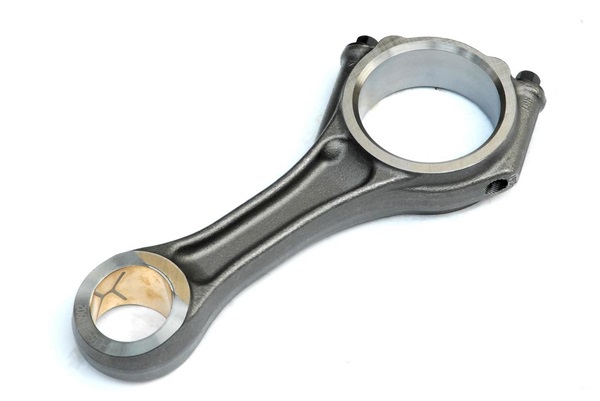
Forged products have the characteristics of high load capacity, long life, and strong adaptability to harsh working conditions. They can be widely used in oil and gas exploration, wind power generation, metallurgical machinery, engineering machinery, ships, pressure vessels, nuclear power, and other industries. Today, we will introduce the forging process in detail, including its definition, classification, and application.
Table of Content
- Definition of Forging
- Classification of the Forging Process
- Forging Material
- The Main Characteristics of Forgings
- Application of Forgings

Definition of Forging
Forging is a processing method that uses forging machinery to apply pressure to metal blanks to cause plastic deformation to obtain forgings with certain mechanical properties, certain shapes, and sizes.
Forging can eliminate defects such as as-cast porosity produced by the metal during the smelting process. At the same time, due to the preservation of complete metal flow lines, the mechanical properties of forgings are better than castings of the same material. In machinery, forgings are often used for important parts with high loads and severe working conditions.
Classification of the Forging Process
According to the forging temperature
Forging can be divided into hot forging, warm forging, and cold forging, according to the forging temperature.
The starting recrystallization temperature of steel is about 727°C, but the industry generally uses 800°C as the dividing line. Hot forging is above 800°C. It is called warm forging or semi-hot forging between 300 and 800°C, and forging carried out at room temperature is called cold forging. Forgings in most industries are processed by hot forging. Warm forging and cold forging are mainly used for forging parts such as automobiles and general machinery. Warm forging and cold forging processes can achieve effective material savings.
According to the production tool
According to different production tools, forging technology can be divided into free forging, die forging, ring rolling, and special forging.
Free forging
Free forging refers to the processing method of using simple general-purpose tools or directly applying an external force to the blank between the upper and lower anvils of the forging equipment to deform the blank to obtain forgings with the required geometric shape and internal quality.
Free forging adopts the hot forging method. The basic process of free forging includes upsetting, drawing, punching, cutting, bending, twisting, shifting, and forging.
Free forging mainly produces forgings in small batches. Forging equipment such as forging hammers and free-forging hydraulic presses are used to form blanks to obtain qualified forgings.
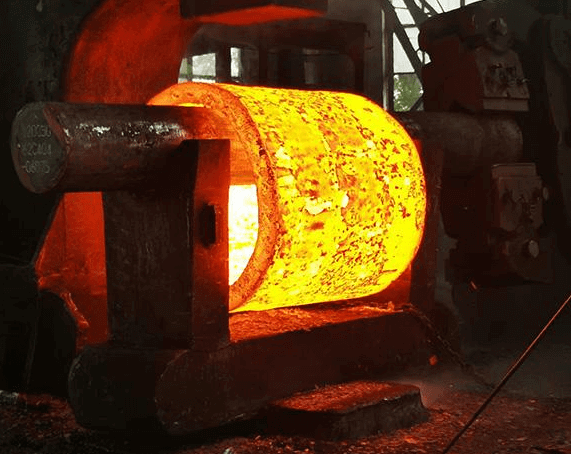
Die forging
Die forging means that the metal blank is compressed and deformed in a forging die chamber with a certain shape to obtain a forging. Die forging is generally used to produce parts with small weights and large batches. Die forging is divided into open-die forging and closed-die forging.
Open die forging is the deformed flow of metal within a cavity that is not completely restricted, with a die having a flash groove that accommodates excess metal. When the upper and lower molds are closed, on the one hand, the metal flows to the cavity to fill the shape, and on the other hand, the excess metal flows out of the cavity and becomes a flash.
Closed die forging means no flash die forging. Generally, during the forging process, the gap between the upper die and the lower die remains unchanged. And the billet is formed in a closed die cavity around it, without generating lateral flash. A small amount of excess material will form longitudinal flying spurs, which are removed in a subsequent process.
Zhengxi is a professional forging machine manufacturer with high-quality open die forging presses and closed die forging presses. You can contact us for more information about die forging machines.
Grind ring
Ring rolling refers to the production of ring parts of different diameters through special equipment ring rolling machines, and is also used to produce wheel-shaped parts such as automobile wheels and train wheels.
Special forging
Special forging includes roll forging, cross wedge rolling, radial forging, liquid die forging, and other forging methods. These methods are more suitable for the production of parts with certain special shapes. Roll forging, for example, can be used as an effective performing process, significantly reducing subsequent forming pressures. Cross-wedge rolling can produce steel balls, transmission shafts, and other parts. Radial forging can produce large forgings such as barrels and stepped shafts.
According to the movement mode of the forging die, forging can be divided into pendulum rolling, pendulum swivel forging, roll forging, cross wedge rolling, ring rolling and cross rolling.

Forging Material
Forging materials are mainly carbon steel and alloy steel with various components. Followed by aluminum, magnesium, copper, titanium, etc., and their alloys. Deformed alloys of iron-based superalloys, nickel-based superalloys, and cobalt-based superalloys are also finished by forging or rolling, but these alloys are relatively difficult to forge due to their relatively narrow plastic zones. There are strict requirements on the heating temperature, starting forging temperature, and final forging temperature of different materials.
The original state of the material is bar stock, ingot, metal powder, and liquid metal. The ratio of the cross-sectional area of the metal before deformation to the cross-sectional area after deformation is called the forging ratio.
Correct selection of forging ratio, reasonable heating temperature and holding time, reasonable initial forging temperature and final forging temperature, reasonable deformation amount and deformation speed have a great relationship with improving product quality and reducing costs.
The Main Characteristics of Forgings
The products manufactured by the forging process are called forgings. Forgings have the following advantages.
- Large weight range. Forgings range in size from a few grams to hundreds of tons.
- Higher quality than castings. The mechanical properties of forgings are better than castings, and they can withstand large impact forces and other heavy loads. Therefore, forgings are used for all important and stressed parts.
- The lightest. Under the premise of ensuring the design strength, forgings are lighter than castings, which reduces the weight of the machine itself. It is of great significance to means of transportation, aircraft, vehicles, and aerospace equipment.
- Save raw materials. For example, for a crankshaft with a static weight of 17kg used in automobiles, when the rolled material is cut and forged, the chips account for 189% of the weight of the crankshaft, but when die forging is used, the chips only account for 30%, and the machining time is shortened by 1/6. Precision-forged forgings can not only save more raw materials but also save more machining hours.
- High productivity. For example, using two hot forging presses to forge radial thrust bearings can replace 30 automatic cutting machine tools. When using an upsetting automatic machine to produce M24 nuts, the productivity is 17.5 times that of a six-axis automatic lathe.
- Free forging has great flexibility. Therefore, some repair factories widely use forging methods to produce various accessories.

Application of Forgings
Forging production is widely used in metallurgy, mining, automobiles, tractors, harvesting machinery, petroleum, chemical industry, aviation, aerospace, weapons, and other industrial sectors.
In the field of machinery manufacturing, turbine generator shafts, rotors, impellers, blades, retaining rings, large hydraulic press columns, high-pressure cylinders, rolling mill rolls, internal combustion engine crankshafts, connecting rods, gears, bearings, and artillery in the defense industry, etc. are all produced by forging.
Zhengxi is a well-known forging machine manufacturer in China, providing various types of forging presses, including free forging machines, die forging machines, hot forging machines, cold forging machines, and warm forging machines, etc. If you have any needs, please contact us.



