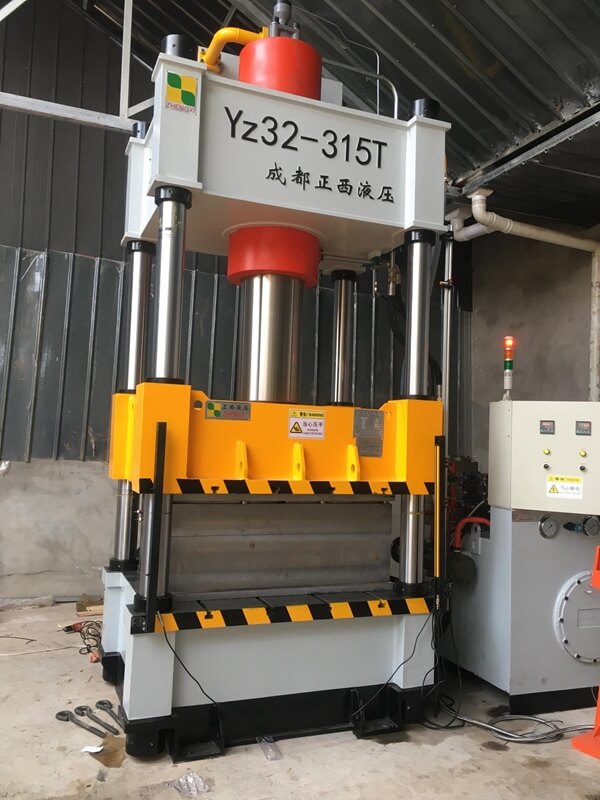
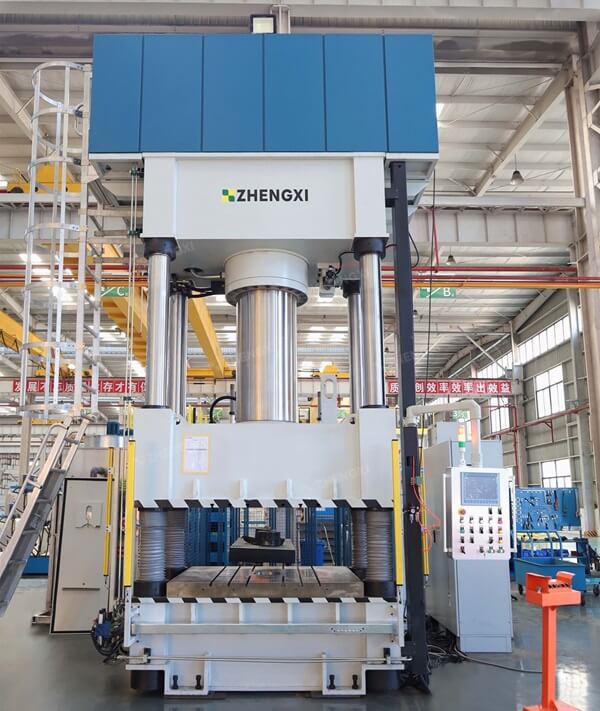
Multi-directional die forging technology, or multi-plunger die forging, is a comprehensive process that integrates extrusion and die forging. It uses a separable die to obtain complex forgings with no burrs, no draft angle or small draft angle, multiple branches, or inner cavities under the action of a single stroke of the multi-directional die forging press.
Compared with ordinary die forging, it can reduce the number of processes, save energy, improve the performance of forgings, and have many unique advantages in achieving forging refinement, improving product quality, and increasing labor productivity.

Forming Principle of Multi-directional Die Forging
Multidirectional die forgings are formed in a closed cavity with four dies that can be divided. It can be divided into four dies, and then one or more punches move in the horizontal or vertical direction to form the blank in the die. When the blank is formed, some metal flows parallel to the direction of movement of the punch, so some metal flows perpendicular to the direction of movement of the punch or at a certain angle to the direction of movement. In this way, forgings with multiple split mold shapes, multiple branches, precise calibers in the cavity, and complex shapes are formed.
The prerequisite for multi-directional die forging is having a multi-directional die forging press. The multi-directional die-forging press frame is designed at a certain angle in the left and right directions. The frame uses steel wire winding to provide preload in the vertical and horizontal directions of the frame. The multi-directional die forging hydraulic press can use punches in different directions and orders to extrude the blank in the closed die to fill the die cavity well. After forging, the die is separated, and the forging is removed from the die cavity.
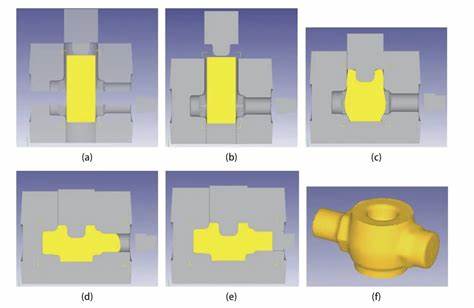
Types of Multi-directional Forging
According to the different die-splitting methods of forgings, multi-directional die forging can be divided into three types: vertical die splitting, horizontal die splitting, and vertical and horizontal combined die splitting (called compound die splitting).
(1) Vertical die splitting
Vertical die splitting is to fix the left and right dies on the horizontal cylinder piston of the press. Fix the vertical punch on the piston of the vertical perforating cylinder. Press the left and right dies with the horizontal cylinder piston. Put the blank into the die cavity and squeeze the blank with the vertical punch so that the blank fills the die cavity. After forging, the vertical punch returns, the horizontal cylinder returns to open the left and right dies, and the forging is removed from the die cavity.
(2) Horizontal die splitting
In horizontal die splitting, the upper and lower dies are fixed on the movable and lower crossbeam. The vertical punch is fixed on the piston of the vertical perforating cylinder, and the horizontal punch is fixed on the piston of the horizontal perforating cylinder. After the blank is placed in the lower die cavity, the upper die presses the upper and lower dies under the action of the movable crossbeam. The vertical and horizontal punches extrude the blank, so the blank fills the mold cavity. After forging is completed, the vertical and horizontal punches return, respectively. The return stroke separates the upper and lower molds, removing the forging from the mold cavity.
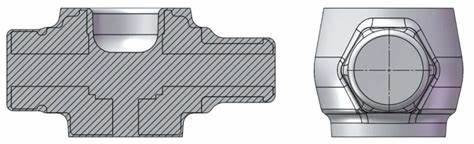
(3) Compound die splitting
Compound mold splitting is when the left and right molds are closed and pressed after the blank is placed in the lower mold cavity. The upper punch extrudes the blank to deform, and the horizontal punch extrudes the blank to make the metal completely fill the mold cavity. After forging, the left and right molds are separated, and the forging is removed from the lower mold cavity.
When formulating the multi-directional die forging process for forgings, the first thing to do is to correctly select the parting method and reasonably determine the parting surface. Usually, the parting method and the position of the parting surface are determined comprehensively based on the shape, size, and structural characteristics of the forgings, such as the complexity of the forging shape, the size of the vertical and horizontal projection area, the requirement for the presence or absence of a forming cavity, the ratio of the inner hole length to the hole diameter, etc., combined with the existing multi-directional die forging hydraulic press force parameters, plunger stroke, and die installation space conditions.
Technical Characteristics of Multi-directional Die Forging
Multi-directional die forging is essentially extrusion-based, combining extrusion and die forging. Compared with ordinary die forging, multi-directional die forging has the following characteristics:
(1) It can form forgings with complex structures and shapes, significantly improve material utilization, and shorten machining hours.
Multidirectional die forging can obtain forgings with complex shapes, precise dimensions, no forging flash, and no holes so that the forgings can be as close as possible to the shape and size of the finished parts. This can significantly improve the material utilization of parts, shorten machining hours, and significantly reduce forging costs. It is the optimal forging process for producing forgings with complex structural shapes.
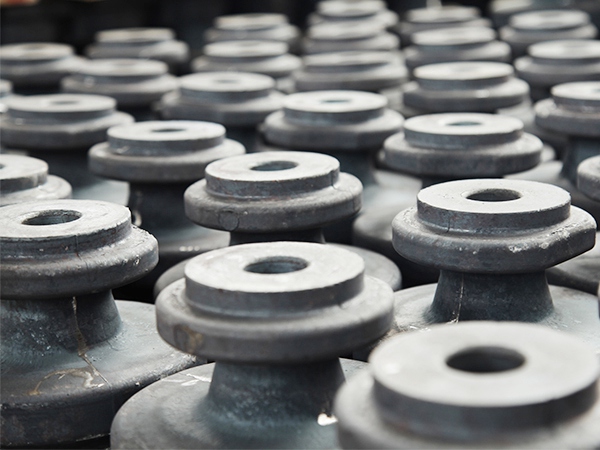

(2) The distribution of metal streamlines is reasonable, and the performance of forgings is improved.
Multi-directional die forging does not produce flash, and the end of the forging streamline will not be exposed due to edge trimming. Therefore, the metal streamlines of multi-directional die forgings are distributed along the contour of the forging, which is beneficial to improving the forging’s mechanical properties. In addition, this is particularly important to improving the stress corrosion resistance of parts.
(3) The blank can be forged into forgings by heating only once, improving production efficiency and reducing energy consumption.
The bad material must only be heated once during multi-directional die-forging production. The press can forge the blank into a forging in one working stroke. Therefore, it can reduce production processes, improve production efficiency, save energy consumption, reduce heating equipment, reduce metal material burning loss, forging surface decarburization, and reduce alloy element depletion.
(4) Suitable for producing die forgings with narrow forging temperature and low plasticity materials.
The materials for some important key parts in mechanical products are often alloy steels and alloys with narrow forging temperatures and low plasticity that are difficult to deform, such as stainless steel, high-temperature alloys, titanium alloys, etc. During ordinary die forging of this type of metal material, tensile stress will occur due to the stress state, which will cause the forging to crack and be scrapped. During multi-directional die forging, the blank is deformed under strong three-dimensional compressive stress, which improves the plasticity of the metal and is suitable for the die forging of hard-to-deform metal materials.
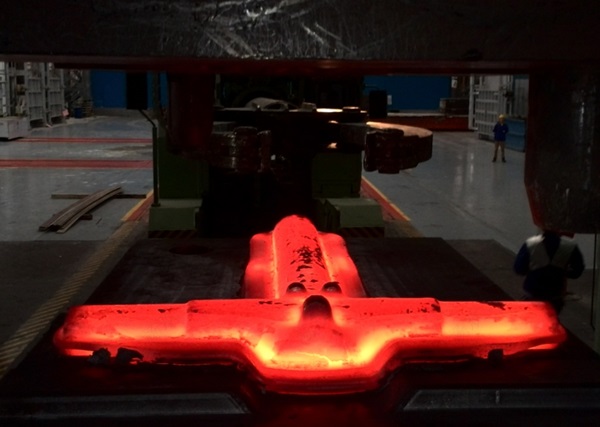
Due to the above characteristics of multi-directional die forging, in the aviation, petroleum, chemical industry, automobile and tractor manufacturing, atomic energy industry, hollow frames, pistons, shafts, cylindrical parts, large valve bodies, pipe joints, aircraft landing gear, engine casings, disc-shaft assemblies, and other forgings, multi-directional die forging technology has begun to be used for production.
Due to the above characteristics of multi-directional die forging, it has begun to be used for production in the aviation, petroleum, chemical industry, automobile and tractor manufacturing, atomic energy industry, hollow frames, pistons, shafts, cylindrical parts, large valve bodies, pipe joints, aircraft landing gear, engine casings, disc-shaft assemblies, and other forgings.
Zhengxi is a famous forging press manufacturer in China and can provide professional forging knowledge. If you have any needs, please contact us!