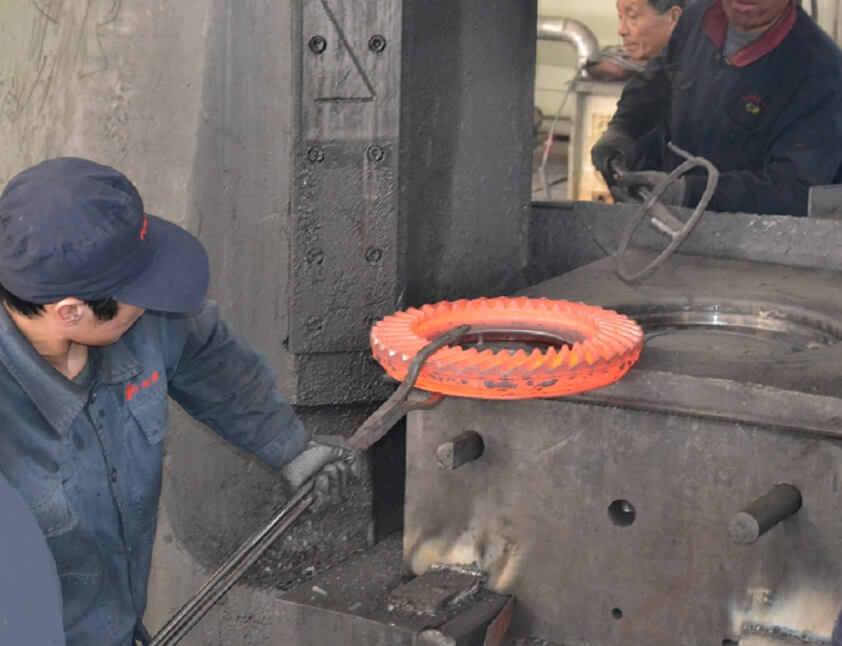
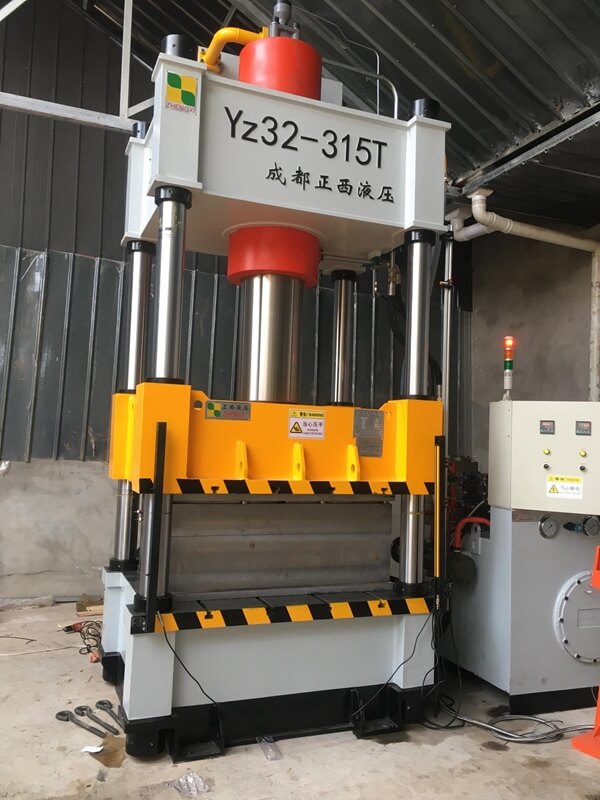
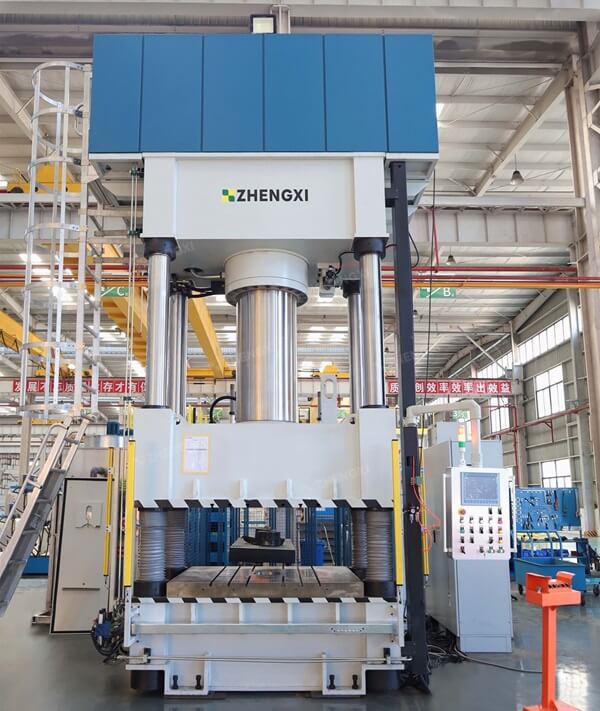
A gear is a mechanical element with teeth on the rim that can continuously mesh to transmit motion and power. Gear forging products are mainly used in mining machinery, the petrochemical industry, automobile manufacturing, and other industries. More than 90% of them are automotive forgings. Among them, cold-temperature precision forgings account for about 5.2% of the total forgings.
The purpose of precision gear forging is to directly produce gears without subsequent cutting. If it can be forged at room temperature, the shape and size of the gear can be easily controlled, and errors caused by high temperatures can be avoided. Currently, many bevel gears and small cylindrical gears are manufactured using this method. Cylindrical spur and helical gears can also be manufactured by cold extrusion when the overall dimensions are appropriate.

Forging can improve material utilization, increase productivity, improve the mechanical properties of gears, reduce costs, and enhance market competitiveness. Especially for mass production in the automotive industry, precision gear forging has greater benefits and potential.
At present, the generally accepted process method is a combination of hot forging, warm forging, and cold forging. Hot forging and warm forging can achieve high efficiency and high material utilization, while cold forging can correct the errors of hot forging and warm forging and improve surface quality. At the same time, the cold treatment process can also obtain residual compressive stress on the tooth surface and increase the service life of the gear.
Overall Process Plan for Gear Forging Production Line
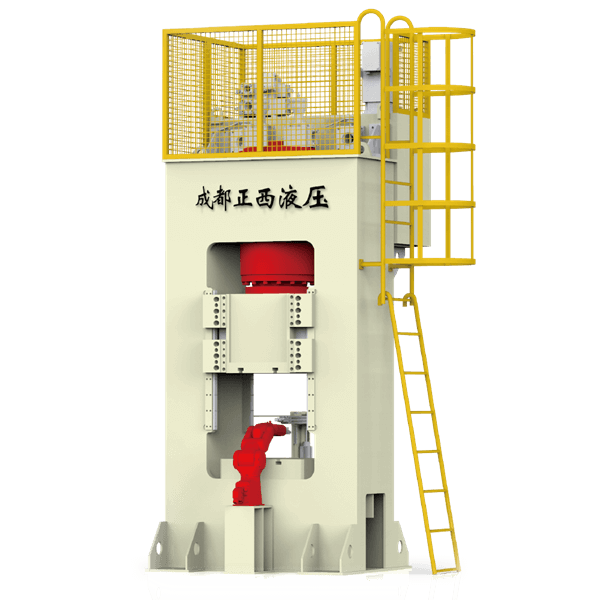
According to the characteristics of precision forging gear production, Zhengxi’s 1600T hot die forging press production line is recommended. It mainly includes a 1600T hot die forging press, automatic feeding device, Y conveyor belt, etc. It is used for multi-station automatic forging production of precision forged gear forgings, using four-station warm precision forging and cold finishing. The hot forging frequency is 8-10 times per minute.
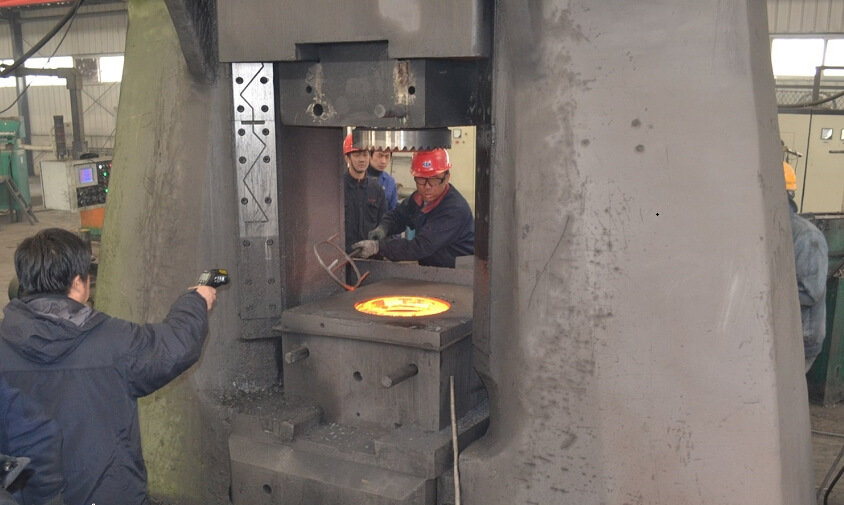

The process technology plan is as follows:
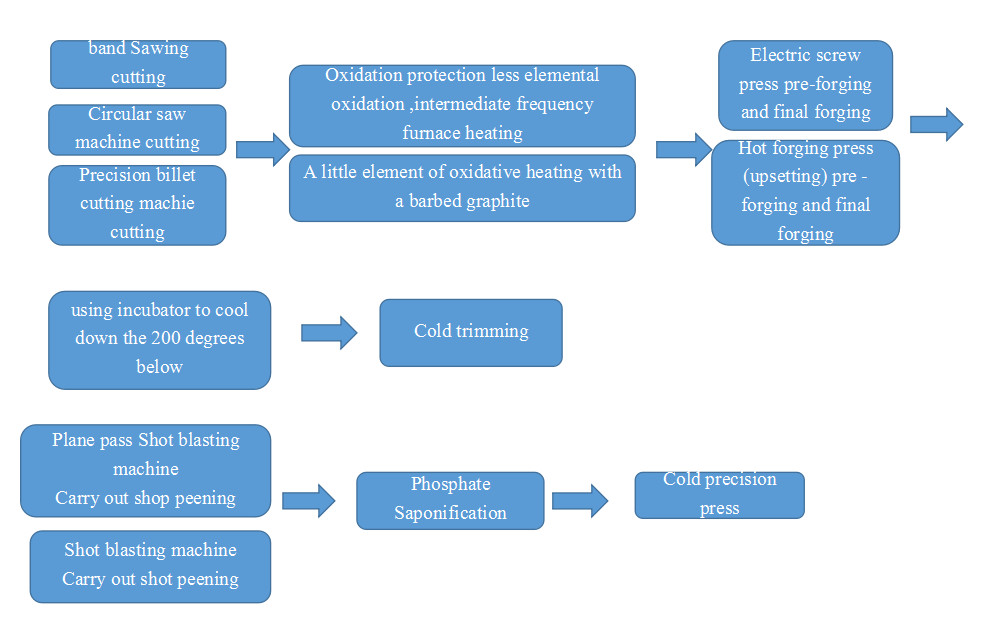
- Use a forklift to place the precision blanked bars into the bin tip of the medium-frequency induction heating furnace. Transferred to the stepper automatic loading machine. Automatically transport the blanks to the discharging conveyor chain. Enter the pinch roller feeding system. The bar material is heated to the set temperature by the heating induction coil at a continuous and uniform predetermined speed. Through the temperature sorting mechanism, unqualified bar materials are eliminated, and qualified bar materials are sent to the red parts conveyor belt through the rapid discharging mechanism.
- The red-piece conveyor belt sends the bar material into the turning trough at the beginning of the automatic conveying device to make the bar material stand upright. Convenient for clamping of conveyor devices.
- Automatic conveying devices (robots) are installed on both sides of the hot die forging press and are responsible for the automatic conveying of forgings.
- The hot die forging press has four forging stations: upsetting, pre-forging, final forging, and trimming.
- The mold and mold base are installed on the hot die forging press and are lubricated and cooled through an automatic spray device.
- After forging is completed, the forgings are transferred to the designated material frame through the conveyor belt.
Gear Process Block Diagram
Main Technical Parameters of Forging Press
| Name | Unit | Specification |
| Nominal force | KN | 16000 |
| Slider stroke | mm | 280 |
| Number of slide strokes | SPM | 90 |
| Single production frequency | times/minute | 15 |
| Maximum closed height | mm | 875 |
| Mold height adjustment amount | mm | 16 |
| Workbench size (left and right x front and rear) | mm | 1050 x 1400 |
| Slider bottom size (left and right x front and back) | mm | 1030x 1140 |
| Main motor (power) | KW | 95 |
| Ejecting device (pressure) | KN | 80 |
| Ejecting device (stroke) | mm | 37 |
| Lower ejection device (pressure) | KN | 240 |
| Lower ejector device (stroke) | mm | 37 |
| Workstation arrangement (number of workstations) | 4 | |
| Workstation arrangement (workstation spacing) | mm | 240 |
| Overall dimensions (left and right x front and rear x height above ground) | mm | 4100 x 3500 x 7050 |
Main Features of Hot Die Forging Press
- Frame: adopts an integral casting body. There are side windows on both sides of the frame to facilitate horizontal feeding. The rough and processed parts are inspected separately to ensure that the welded parts are defect-free.
- Main drive: The main drive consists of a motor, belt drive, flywheel, rolling bearing, belt drive tensioning mechanism, and connections.
Parts, etc. - Slider: The slider is made of cast steel, and the casting needs to be heat-treated. The slider guide adopts an X-shaped long guide rail structure. The guide length is long, the guide surface is large, the guide precision is high, and the ability to withstand eccentric loads is strong. Because the X-shaped guide rail is less affected by thermal expansion, in the production environment of hot processing, it is necessary to ensure the guide rail clearance during the forging process and obtain higher guiding accuracy to improve the accuracy of forgings.
- Connecting rod: The connecting rod is made of chromium-molybdenum alloy cast steel, and the castings are heat-treated. The connecting rod adopts a double-point structure to improve the rigidity of the hot die forging press and realize multi-station forging.
- Eccentric shaft and pressure pin: The eccentric shaft is made of high-quality alloy steel forgings, and the pressure pin is made of high-quality alloy steel forgings. Forgings must be forged by units with quality qualifications. After rough machining, quenching and tempering treatment is required to enhance its yield limit, elongation, etc. The surface roughness is finally polished.