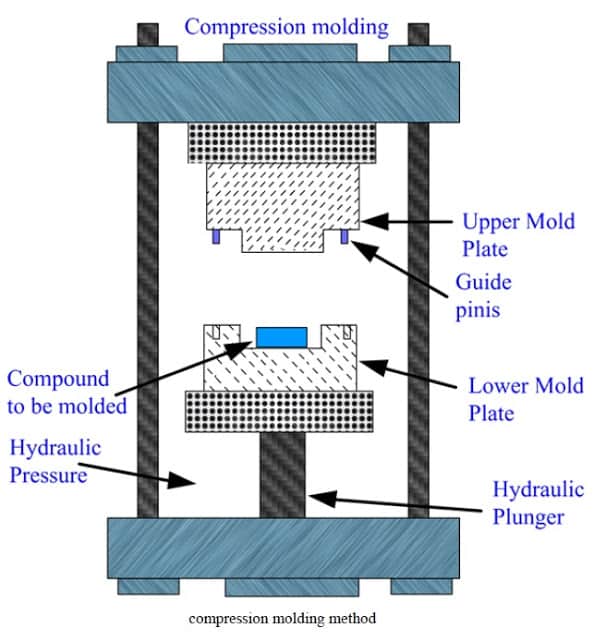
Compression molding, also known as composite compression moulding, is adding powdery or loose granular solid plastics directly into the mold, and gradually softening and melting them by heating and pressing. Then it is molded according to the shape of the cavity and solidified into a plastic part. Mainly used for forming thermosetting plastics, but also for thermoplastics.
Compared with injection molding, the advantage of compression molding is that ordinary hydraulic presses can be used, and the structure of the compression mold is simple (no pouring system). In addition, the internal orientation structure of compressed plastic parts is less, the shrinkage rate of plastic parts is small, and the performance is uniform. Its disadvantages are long forming cycles, low production efficiency, high labor intensity, difficulty to control the precision of plastic parts, short mold life, and difficult to realize automatic production.
Table of Content
1. Principle of Compression Molding
2. Compression Molding Process
3. Compression Molding Process Parameters
4. Compression Molding Features
5. Compression Molding Applications

Principle of Compression Molding
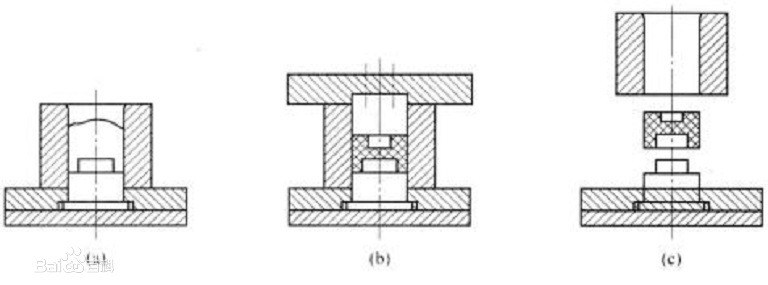
The principle of composite compression molding is shown in Figure 1. When molding, the powdery, granular, crumb, or fibrous thermosetting plastic raw materials are directly added to the open mold feeding chamber, as shown in a) in Figure 1. The mold is then closed and heated to melt the plastic. Under the action of the clamping pressure, the molten plastic fills the cavity everywhere, as shown in b) in Figure 1. At this time, the plastic in the cavity produces a chemical cross-linking reaction, so that the molten plastic is gradually transformed into an infusible hardened and shaped plastic part. Finally, de-molding takes the plastic part out of the mold, as shown in c in Figure 1.
Compression Molding Process
(1) Preparation before molding
Thermosetting plastics are relatively easy to absorb moisture and are prone to moisture during storage. Therefore, it should be preheated and dried before processing the plastic. At the same time, due to the relatively large specific volume of thermosetting plastics, in order to make the molding process go smoothly, sometimes the plastics must be pre-pressed.
① Preheating and drying. Thermoset plastics should be heated prior to molding. There are two purposes of heating: one is to preheat the plastic, so as to provide a certain temperature of heat material to the compression mold so that the plastic is heated evenly in the mold and shorten the compression molding cycle. The second is to dry the plastic to prevent excessive moisture and low molecular volatiles in the plastic to ensure the molding quality of the plastic parts.
② Preloading. Pre-compression refers to compacting loose powdery, granular, crumb-like, sheet-like, or long-fibrous molding materials into plastics with a certain weight and shape at room temperature or slightly higher than room temperature before compression molding so that they can be placed into the compression mold relatively easily. The shape of the pre-pressed blank is generally in the shape of a disc or a disc, and it can also be pressed into a shape similar to a plastic part. The preload pressure can usually be selected within 40~200MPa. After pre-pressing, the density of the blank should preferably reach about 800k of the density of the plastic part, so as to ensure that the blank has a certain strength.
(2) Compression molding process
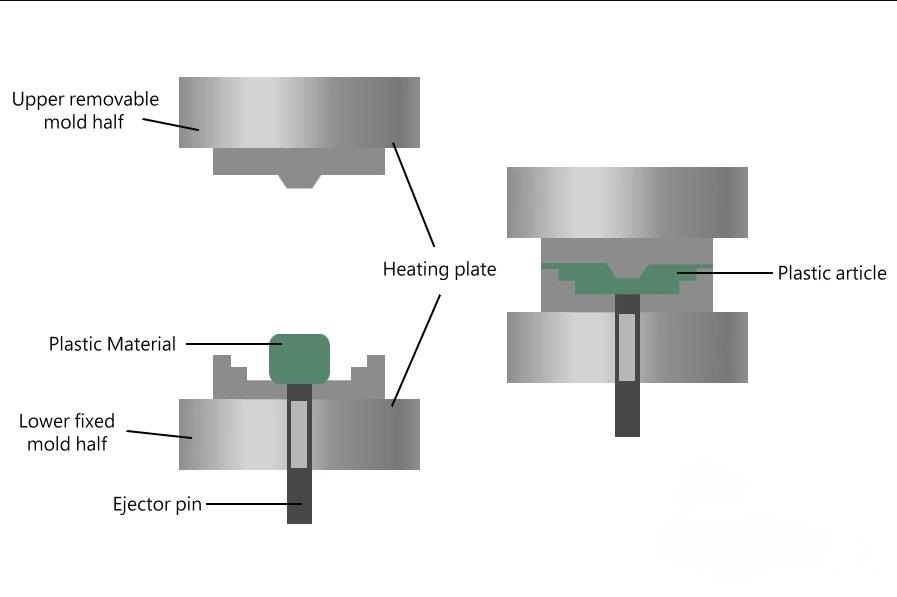
After the mold is installed on the hydraulic press, it needs to be preheated. If the plastic part has an insert, the preheated insert should be placed in the mold cavity before feeding. The molding process of thermosetting plastics can generally be divided into several stages such as feeding, mold closing, exhausting, curing, and demolding.
(3) Processing after compression
After the plastic parts are molded, the mold should be cleaned, and sometimes the plastic parts should be post-processed.
① Mold cleaning. After de-molding, use copper picks or copper brushes to remove debris and flashes left in the mold. Then blow out the mold cavity with compressed air. If these sundries are left in the next molded plastic part, it will seriously affect the quality of the plastic part.
②Post-processing of plastic parts. The post-processing of plastic parts mainly refers to annealing treatment. Its main function is to eliminate internal stress, improve the dimensional stability of plastic parts, and reduce the deformation and cracking of plastic parts. Further cross-linking and curing can improve the electrical and mechanical properties of plastic parts. The annealing specification should be determined according to the material, shape, insert, etc. of the plastic part. For plastic parts with thick walls and widely different wall thicknesses and easy deformation, it is advisable to use a low temperature and long time for annealing treatment.
Compression Molding Process Parameters
The quality and performance of plastic parts are not only affected by the properties of plastic raw materials and the size of the mold structure but are also related to the formulation and control of molding process parameters. These are the three elements of molding that are often said in production: temperature, pressure, and time.
1) Molding temperature
Molding temperature refers to the mold temperature required for pressing. At this temperature, the plastic melt flows in the cavity fills the cavity, and solidifies. The mold temperature is not equal to the temperature of the plastic melt in the cavity.
For thermosetting plastics, the maximum temperature of the plastic melt is higher than the mold temperature due to the exothermic result of the plastic crosslinking reaction.
When thermoplastics are molded, the temperature of the plastic melt in the cavity is limited by the mold temperature. If the molding temperature is too high, although the curing time is short, it will make it difficult to fill the mold, making the surface of the plastic part dull and dull, and even swelling, deformation, and cracking. If the molding temperature is too low, the curing time will be slow and the molding time will be long. Therefore, the determination of mold temperature should comprehensively consider various factors, which is also key to ensuring the quality of plastic parts molding.
2) Molding pressure
Molding pressure refers to the unit pressure of the press on the projected area of the plastic part during compression molding. Its function is to force the plastic melt to flow and fill the mold cavity. Avoid defects such as bubbles and loose structures inside plastic parts due to low molecular volatiles. Ensure that plastic parts have a fixed shape and size, prevent deformation, and improve internal quality.
3) Time
When thermosetting plastics are compressed and molded, they need to be kept at a certain temperature and pressure for a certain period of time before they can be fully cross-linked and solidified to become excellent plastic parts. This period of time is called compression time.
The compression time is related to the type of plastic (resin type, volatile matter content, etc.), the shape of the plastic part, the process conditions of compression molding (temperature, pressure), and the operation steps (whether to exhaust, precompress, preheat), etc. As the compression molding temperature increases, the plastic solidifies faster and the required compression time decreases. An increase in compression pressure also decreases compression time, but not as much as an increase in temperature. In addition, the compression time will increase with the increase of the wall thickness of the plastic part.
The length of compression time has a great influence on the performance of plastic parts. If the compression time is too short, the hardening of the plastic is insufficient (undercooked), the appearance quality of the plastic part is poor, the mechanical properties are reduced, and it is easy to deform. Appropriately increasing the compression time can reduce the shrinkage of plastic parts and improve their heat resistance and other physical and chemical properties. However, if the compression time is too long, it will not only reduce productivity, but also make the plastic parts shrink too much, increase the internal stress, and the plastic parts are easy to break. Generally, the compression time of phenolic plastic is 1~2min, and that of silicone plastic is 2~7min.
Compression Molding Features
Compression molding is mainly used for the molding of thermosetting plastics. The advantages of compression molding over injection molding are:
Can be produced with ordinary hydraulic press machines.
Because the compression mold has no gating system, the mold structure is relatively simple.
There are few orientation structures in the plastic part, the degree of orientation is low, and the performance is relatively uniform.
The molding shrinkage rate is small, and some fillers with crumbs, flakes, or long fibers can be produced.
Compression Molding Applications
Compression molding is specially used for the processing of special materials, such as parts with special requirements in terms of thermal and electrical insulation. Commonly used are: electronic equipment housings, kitchen equipment, ashtrays, handles, lamps, etc. Thermosets are particularly useful for battery covers in electric vehicles, as they can provide the required electrical insulation and stability of the part.
Thermoset rubbers can be applied in processes such as compression molding, injection molding, and vacuum casting. It can be used to produce a range of products such as keypads, seals, and gaskets. Logos, decorations, soles, and other sports items on running shoes can also be made in this way. In addition, the housing of electronic equipment, which is widely used, is molded from a piece of rubber, which can be better waterproof and resistant to damage. This is especially valuable for handheld navigation devices and other portable electronic devices.